|
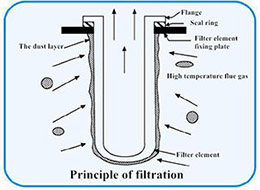 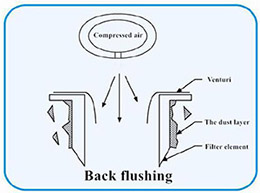
n Technical principle
In addition to filtering dust, ceramic filters react with different additives, such as calcium base and sodium base alkaline powders, to remove acid gas (SO2, HCL, HF, etc.), adding ammonia/urea to remove nitrogen oxides.
n Process flow diagram
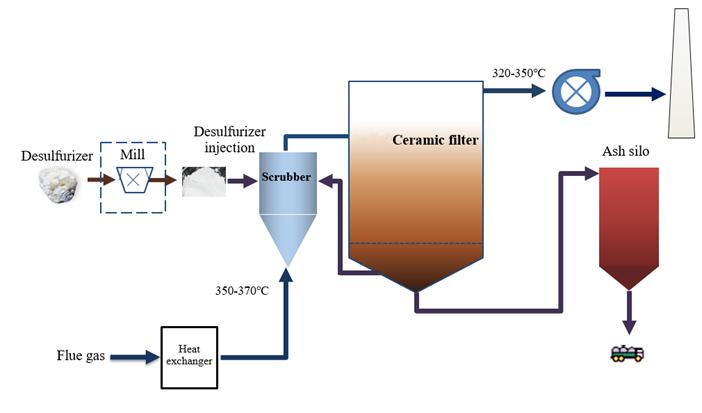
n Technological process
When the flue gas enters the integrated system of desulfurization, denitrification and dust removal after cooling of the waste heat boiler, SO3, SO2, HCl, HF and arsenic are removed by entering the flue gas pretreatment tower (calcium or sodium-based alkaline powder is used as the removal agent). Ammonia (ammonia gas/ ammonia water/urea) is injected into the venturi outlet of the scrubber. After full mixing, the flue gas enters the catalytic ceramic fiber filter, under the action of the catalyst contained in the catalytic ceramic candles, the nitrogen oxides in the flue gas of the dust collector react with ammonia to produce nitrogen and water. The purified flue gas is sent to the boiler to recover heat or the chimney to discharge directly through the induced draft fan.
n Technical advantage
p The system has the advantages of simple process, convenient operation and the equipment occupies a small area. Especially suitable for furnace gas treatment with volume ≤50000 Nm3/h.
p It is suitable for high-temperature gas, simple operation, low maintenance cost, dust emission < 5mg/Nm3.
p Compared with the traditional filter bag, the ceramic filter candle has a longer service life (more than 5 years).
p The catalyst distributes evenly in the ceramic filter, which is more effective in catalyzing reaction, less ammonia consumption, and the denitrification effect meets the demand of ultra-low emission.
p The alkaline dust layer is formed on the surface of the filter candle to achieve the synergistic removal of multi-pollutants (NOx, SOx, HCl, HF, dust, etc.)
|




